whitening
Most natural fibers such as cotton, linen, wool and silk, depending on the type of environment and growing conditions, after the stage of washing and removing impurities, have natural pigments or pigments, which if these colors are removed by bleaching However, the quality and shade of the printed or dyed products and the transparency and whiteness of the colorless and pale product or the white background for fabric printing will undergo changes. For example, if the yellow color of cotton fibers is not removed during dyeing and mixing with a color such as blue, green spots will be created on the product, which is not desirable.In some cases, optical bleaches are used for more whiteness in natural, recycled and synthetic fibers. Optical bleaches complement bleaching and make fibers whiter and more transparent. Always consider this point in cases where the fabric is to be dyed with dark matte colors, there is no need for strong bleaching. Today, in order to reduce the consumption of water, energy and consumables, significantly reduce the amount of starch on the fabric, increase the degree of whiteness of the fabric, reduce the finished price of the product, reduce industrial waste and solve environmental problems, simultaneous baking and bleaching of textile products is considered. Is.
Baking and bleaching stages of cellulose fabric at the same time
Bleaching of cellulose products
The most important cellulosic product that undergoes bleaching includes cotton, linen, recycled products such as cellulose acetate or a mixture of cotton fibers and recycled cellulose. Cellulose fibers are often bleached by oxidizing agents such as hydrogen peroxide, brine, and sodium chlorite (oxidative bleaching), and reducing agents are used less often.
The most important oxidizing and reducing agents used for bleaching cellulose products are:
1- Hypochlorites (such as sodium hypochlorite (brine liquid) and calcium hypochlorite (bleaching powder)
2- Peroxides such as hydrogen peroxide (hydrogen peroxide), sodium perborate, peracetic acid, sodium peroxide, sodium percarbonate
3- Sodium chlorite
Bleaching cellulose products with hydrogen peroxide (oxygenated water)
One of the most common and suitable materials for bleaching textile products is hydrogen peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide is an oxidizing, odorless, stable and affordable liquid that is indestructible and controllable during storage, consumption, storage and bleaching. Hydrogen peroxide is decomposed by heat and light; Therefore, it is necessary to store it in a cool and dark place in dark containers. Since hydrogen peroxide does not react with cotton impurities; Therefore, without performing the initial cooking and washing process in the presence of alkali at the boiling temperature, the washing process can be done after the bleaching process at a lower cost, so that it leads to saving time and energy, and the strength of the product does not decrease. to be.Metals (catalysts) such as iron, copper and mercury have a catalytic effect in the bleaching bath and cause rapid decomposition of hydrogen peroxide; Therefore, before bleaching with oxygenated water, it is necessary to control the water used so that the amount of these metals in the water does not exceed one milligram per liter. By using suitable active surface materials and hardening materials, these metals can be removed from water to some extent. Hydrogen peroxide is often used in the presence of a substance that stabilizes, reduces, and controls the decomposition rate of hydrogen peroxide, such as organic stabilizers or sodium silicate, and an alkali such as caustic soda to provide bleaching for a pH of about 10-11.
In order to increase the penetration rate of hydrogen peroxide and the speed of bleaching in high-speed bleaching machines, where the opportunity to absorb bleaching substances is less, wetting, moisturizing or penetrating active surface materials are also used in the bathroom.
– The best temperature for bleaching with hydrogen peroxide is about 90 degrees Celsius for 30-90 minutes. Bleaching at a temperature higher than 110 degrees Celsius removes all the fat in the fabric, makes the underside of the fabric rough and reduces the sewing ability of the woven fabric.
– When hydrogen peroxide decomposes in an alkaline environment, it produces perhydroxy ion, which is the main factor in bleaching. The value of hydrogen peroxide is called the volume of oxygen released from a volume of hydrogen peroxide solution. In bleaching, hydrogen peroxide is often used at 27.5 and 35 percent by weight, and the volumetric value of hydrogen peroxide is 100 and 131.
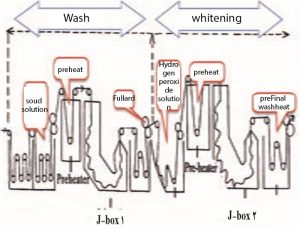
Bleaching by oxygen water method on all types of cellulose goods such as cotton, linen, recycled cellulose, cotton-polyester mixture, cotton-viscose mixture in non-continuous Jigger, winch, Kier, autoclave and semi-continuous pad-batch, continuous machines. Pad-Steam (steam), JBox, ST Guinness, Gunwal, Dangler and… do. Most light and thin fabrics are bleached in rope form and thick, heavy and wrinkled fabrics are bleached in open width. Non-continuous bleaching machines are often dyeing machines.
One of the most widely used semi-continuous bleaching machines is the pad-roll machine, which includes three main parts: the bleaching solution tank, the fullard or pressing rollers, and the thermal chamber. In these machines, the fabric is opened from the fabric carrier roller and after passing through the guide rollers, it enters the tank containing the bleaching solution. The fabric is soaked in the bleaching solution in the tank, and after passing through the tank, it passes between the fullard rollers with a certain cut to remove the excess solution. The fabric is finally wrapped around special rollers in an adjustable and controllable thermal chamber and stays in this tank for a while. The fabric rollers in the thermal chamber are rotated slowly by an electric motor to prevent the bleaching material from accumulating in one spot and causing stains.
One of the most modern continuous whitening machines is the J. BOX machine. The part of this machine where the fabric is piled is in the shape of the letter J in English. In this machine, after being soaked in bleaching solution and passing through the pressure rollers or fullard, the fabric passes through a heat pipe that is heated by steam and finally remains in the machine’s G-box tank for a certain period of time. After the required time, the fabric is removed from the nose of the tank and after passing between two rollers, it enters the washing area. At the end, the fabric enters the drying unit.
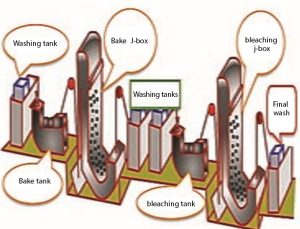
Two-step washing and bleaching operation of fabric in continuous method in J-box
Bleaching of cotton-polyester mixture with 10 to 12 cc per liter of 35% hydrogen peroxide, 10 to 12 cc per liter of sodium silicate and 2 to 4 grams per liter of 100% caustic soda in a G-box machine at a temperature of 95 degrees Celsius. It takes 75 minutes.
After bleaching the cellulosic product, in order to prevent the reduction of the strength of the product and subsequent complications, the bath is emptied and the product is rinsed once. In the second step, half to 1 cc per liter of catalase enzyme is added to the bath and the product is processed at a temperature of 45 to 55 degrees Celsius and the environmental conditions are about 5-7 pH and a time of 30 minutes at a temperature of 70 to 90 degrees Celsius. do In the table below, a sample version of bleaching cotton fabric with oxygenated water in the Keir machine is shown.
A sample version of bleaching cotton fabric in a Kerr machine with hydrogen peroxide

